Aptima™ HBV Quant Assay
Dual-target assay for accurate viral load monitoring of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV).1

Quantitate with Confidence
Deliver trusted results with dual targets across wide linear range and all major HBV genotypes. Running the Aptima HBV Quant assay on the Panther® System combines performance and
excellent automation for viral load monitoring. A combination that delivers sample-to-result within a single integrated instrument.1
Efficient Workflow & Flexible Processing
Sample flexibility EDTA tubes, plasma preparation tubes ACD and EDTA tubes are all validated.1 You can run multiple tests from a single sample. No manual sample preparation with primary tube loading to maintain positive sample identification.
Random Access & Rapid Turnaround Time
No more batching. You can run different test orders from the same sample as they arrive at the laboratory. Rapid turnaround time with first results in just 2 hours, 41 minutes. Prioritizes STAT results.2
Automated Analysis & Dilution Factor
Automated QC analysis with Levey-Jennings plots to track and trend controls. Low sample volume option (240 μL) with automated dilution factor, applying automatic dilution factor instead of manual calculations.2
Simplify and Scale the Future of Diagnostics
The Aptima HBV Quant Assay is part of Panther® Scalable Solutions, a portfolio combining a broad, high performing assay menu with high throughput automation. Designed to flexibly scale to meet your needs, from a single patient result to population-level screening.

Excellent Sensitivity & High Precision
Even with low-level viremia samples.1
5.6 IU/mL
Plasma
Limit of detection (LoD)
4.3 IU/mL
Serum
Limit of detection (LoD)
10 IU/mL*
Lower limit of quantitation (LLoQ)
10-100 millionIU/mL
Linear range
Designed for Confidence1 Across a Wide Dynamic Range
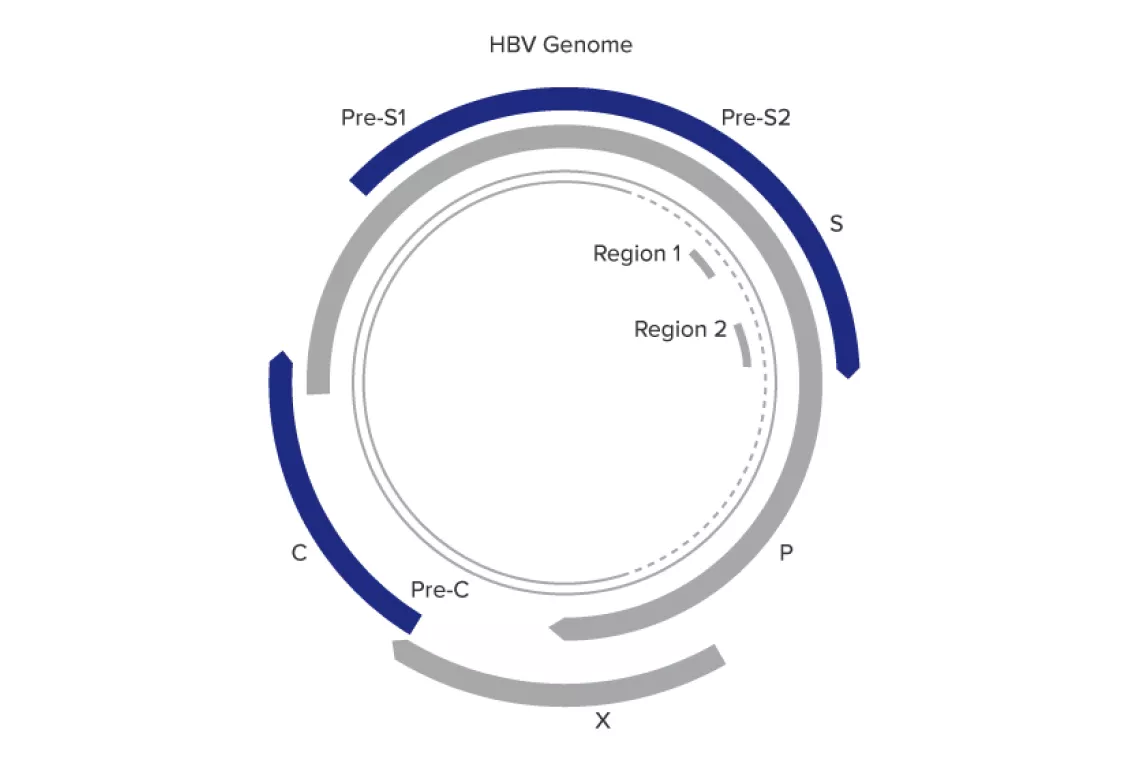
- Targets 2 highly conserved regions in the polymerase and surface genes
- Provides added tolerance to mutations in the HBV genome
- Ensures accurate quantitation over a wide linear range
- Genotype: A-H
- Sample types: plasma and serum
A Global Challenge
Hepatitis B virus (HBV), one of several viruses known to cause hepatitis, has been attributed to lifelong infection, cirrhosis of the liver, liver cancer, liver failure and potentially death. The World Health Organisation (WHO) lists HBV as one of the world’s most common infectious diseases. The prevalence of infection and method of transmission varies greatly around the world. About 1/3 of the world’s population has evidence of past or present HBV infection, with chronic HBV infection occurring in more than 350 million people worldwide.3-5
Evidence. Insight. Collaboration.
Our education portal improves patient care through excellence in education, communication of clinical and scientific evidence, and partnerships with the healthcare community.
Insights
* The LLoQ was established across genotypes (see package insert “Determination of the Lower Limit of Quantitation (LLoQ) Across HCV Genotypes”). This genotype data establishes an overall LLoQ for the assay of 10 IU/mL.
Aptima HBV Quant Assay [package insert] AW-13182-001. Rev.007 San Diego, CA; Hologic, Inc., 2021.
Panther / Panther Fusion Operators Manual AW-26055-001 Rev. 001
Lok AS, McMahon BJ. AASLD Practice Guideline Update. Chronic Hepatitis B: Update 2009. Hepatology. 2009; 50(3):661-662;1-36.
Aspinall EJ, Hawkins G, Fraser A, Hutchinson SJ, Goldberg D. Hepatitis B prevention, diagnosis, treatment and care: a review. Occupational Medicine 2011; 61(8):531-540.
Beckett GA, Ramirez G, Vanderhoff A, et al. Early Identification and Linkage to Care of Persons with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection - Three U.S. Sites, 2012-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014 May 9;63(18);399-401.