Panther Fusion® MRSA Assay
Automate your methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) testing.

Detection & Differentiation
The Panther Fusion MRSA assay brings full automation, efficiency and excellent assay performance to MRSA screening by producing accurate and comprehensive results, providing cost efficiencies to the laboratory and allowing for better patient management.1 The assay detects and differentiates Staphylococcus aureus (SA) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) DNA from nasal swab samples.1
Panther Fusion automatically interprets and reports the results from the following molecular targets; GAPDH, Mec A/C and OrfX/SCC.
GAPDH
Staphylococcus aureus specific housekeeping gene
Mec A/C
A gene that causes methicillin resistance
OrfX/SCC
Indicates the presence of the cassette
Automate your Testing Routine & Deliver Results Faster
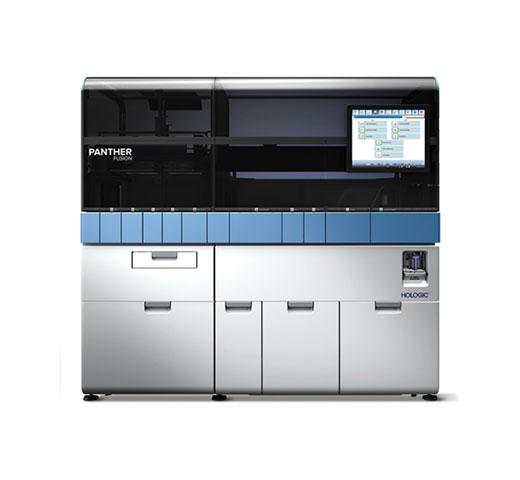
The Panther Fusion MRSA assay leverages the benefits of the Panther Fusion® System, with flexible workflow and improved laboratory efficiency, in comparison to protocols for enrichment followed by culture or LDT.
Rapid Results
Time to first result in 2.4 hours. Five results every 5 mins thereafter. Up to 335 results in 8 hours.1
Workflow Efficiency
Direct loading of ESwab™ nasal samples, enables fully automated sample to result processing.1 Load up to 120 samples at one time. Panther Fusion automatically interprets and reports the results.2
Strain Inclusivity & High Differentiation
Invader Plus® chemistry provides qualitative detection and differentiation of SA and MRSA, broad strain inclusivity, including the Bengal Bay clone, and correct identification of empty cassette variants.1
Low Waste
Unit-dose lyophilized reagents eliminate waste and the need for manual preparation. The ready-to-use, unit-dose format with 60-day onboard stability also helps reduce waste.1

Simplify & Scale the Future of Diagnostics
The Panther Fusion MRSA assay is part of Panther® Scalable Solutions, a portfolio combining a broad, high performing assay menu with high throughput automation. Designed to flexibly scale to meet your needs, from a single patient result to population-level screening.
Proven Performance
Delivering qualitative detection and differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from nasal swab specimens.1
>95% sensitivity
and specificity for the detection of MRSA
>95% sensitivity
and specificity for the detection of SA
Broad strain inclusivity
including the Bengal Bay clone and detection of empty cassette variants
Panther Fusion MRSA Workflow
-
Specimen arrives in lab
-
Replace specimen cap with pierceable cap
-
Load sample(s) onto Panther Fusion
-
Load reagents, if required (60 day onboard stability)
-
Automated Results report: +/- for MRSA & SA
Report results the same day. The time to first result is 2.4 hrs, enabling improved patient management and faster diagnosis.


A Highly Invasive Threat
MRSA is considered a significant cause of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) in the Canada.3 As a result of its highly invasive nature and limited susceptibility to treatment, MRSA is an immense clinical burden with high morbidity and mortality.4 Due to high prevalence among hospitalized patients, accurate and fast identification of MRSA is necessary to initiate effective antimicrobial therapy and slow the spread of MRSA infections.5 Molecular methods for the detection of MRSA have been introduced as a faster alternative to traditional, time-consuming culture methods.
Evidence. Insight. Collaboration.
Our education portal improves patient care through excellence in education, communication of clinical and scientific evidence, and partnerships with the healthcare community.
Insights
- MRSA Assay (Panther Fusion) [Package Insert] AW-22789-001 Rev 001, San Diego, CA; Hologic, Inc., 2023
- Panther / Panther Fusion Operators Manual AW-26055-001 Rev. 001
- https://www.canada.ca/content/dam/phac-aspc/documents/services/reports-publications/canada-communicable-disease-report-ccdr/monthly-issue/2022-48/issue-7-8-july-august-2022/ccdrv48i78a03-eng.pdf. Accessed September 2024
- Ventola, C.L. 2015. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharm Ther. 40(4):277–283.
- Bode, L.G.M., Kluytmans, J.A.J.W., Wertheim, H.F.L., et al. 2010. Preventing surgical-site infections in nasal carriers of Staphylococcusaureus. N Engl J Med. 362(1):9-17.